Effective ventilation is crucial for modern HVAC systems, as it ensures good indoor air quality while keeping thermal comfort in check. By understanding the various types of ventilation systems, homeowners, builders, and HVAC professionals can make better choices for different situations. This guide explores the main categories and important aspects of ventilation systems.
Introduction to Ventilation Systems
Ventilation systems play a vital role in maintaining air quality by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. Proper ventilation helps eliminate pollutants like dust, allergens, moisture, and carbon dioxide while replenishing oxygen levels. Choosing the right system can boost energy efficiency, enhance comfort, and meet health regulations. Ventilation can be achieved through natural methods, mechanical systems, or a combination of both.
Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation depends on passive air movement through openings such as windows, doors, or vents. It takes advantage of pressure differences created by wind and temperature changes to promote airflow. The main benefits include energy savings and a lower dependence on mechanical systems. However, its effectiveness can vary based on climate and building design.
Advantages of Natural Ventilation:
No energy costs
- Low installation and maintenance expenses
- Encourages a healthier indoor atmosphere
Limitations:
- Dependent on weather conditions
- Less effective in urban or polluted environments
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation systems utilize fans and ductwork to manage airflow within a building. These systems ensure consistent air exchange regardless of outside conditions, making them well-suited for modern, airtight structures.
Key Features:
- Regulated airflow rates
- Capability to filter and condition incoming air
- Ideal for spaces with high occupancy or air pollution.
Types of Mechanical Ventilation Systems
Mechanical ventilation can be classified into several types based on how air flows:
Exhaust Ventilation Systems
These systems remove stale air from inside the building, creating a slight vacuum that draws in fresh air through leaks or dedicated vents. They are particularly effective in cold climates but can cause humidity problems in hot, humid areas.
Supply Ventilation Systems
These systems introduce fresh air into the building while expelling stale air through leaks or exhaust points. They help pressurize the building, which can minimize the entry of outdoor pollutants.
Balanced Ventilation Systems
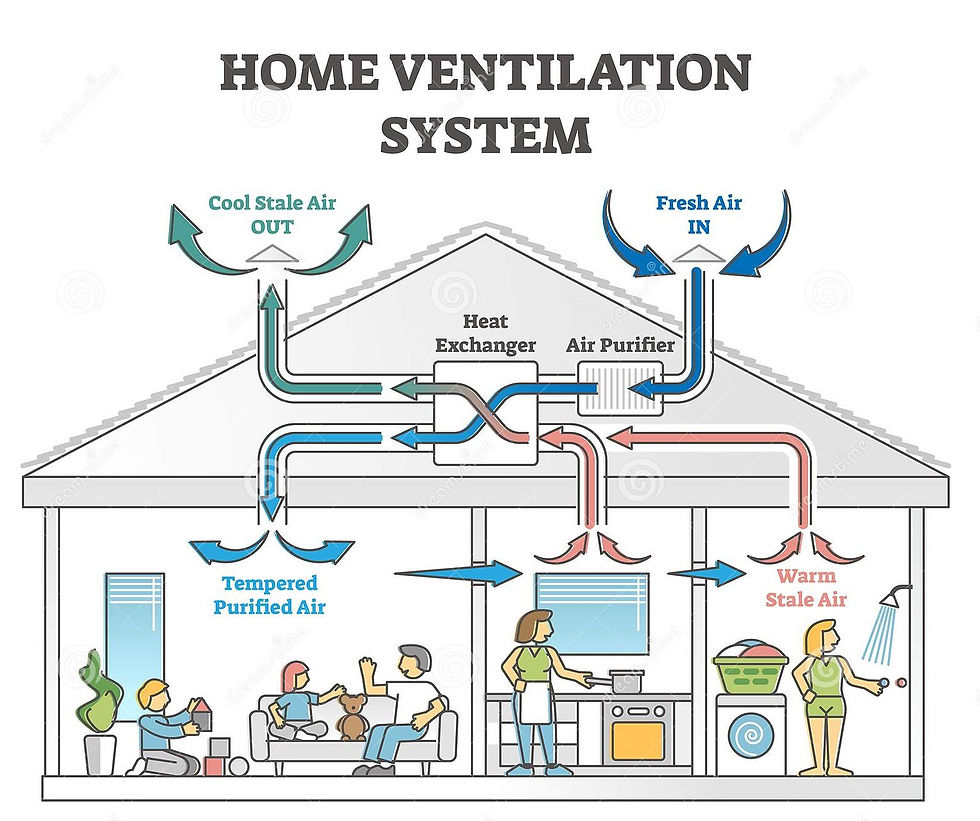
These systems use both supply and exhaust fans to maintain equal airflow in and out of the building. They are often used in conjunction with energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) to enhance efficiency.
Spot Ventilation
This type of ventilation focuses on specific areas, such as kitchens and bathrooms, to eliminate pollutants right at the source. It typically employs exhaust fans for localized air movement.
Hybrid Ventilation Systems
Hybrid systems combine natural and mechanical ventilation, optimizing energy efficiency while ensuring sufficient airflow. They can automatically switch between modes depending on environmental conditions, striking a balance between performance and sustainability.
Benefits of Hybrid Systems:
- Energy-efficient operation
- Versatile and adaptable to different climates
- Improved indoor air quality
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Ventilation System
Choosing the right ventilation system involves several considerations:
Building Design
- Take into account the layout, size, and intended use of the building.
Climate
- Natural ventilation is most effective in mild climates, while mechanical systems are better suited for extreme weather conditions.
Energy Efficiency
- Opt for systems equipped with ERVs or HRVs to recover energy and lower costs.
Air Quality Needs
- Assess specific requirements such as humidity control, filtration, or pollutant removal.
Compliance with Standards
- Make sure the system adheres to local building codes and indoor air quality regulations.
Maintenance of Ventilation Systems
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of ventilation systems. Key tasks include:
- Filter Replacement: Periodically replace or clean filters to maintain proper airflow and prevent contamination.
- Fan and Duct Inspection: Inspect for any blockages, wear, or damage.
- System Balancing: Ensure that airflow is balanced in mechanical systems to prevent pressurization issues.
- Cleaning: Remove dust and debris from ducts, fans, and vents.
- Performance Monitoring: Utilize sensors to monitor air quality and system efficiency.
Conclusion
Ventilation systems play a vital role in creating comfortable and healthy indoor environments. Whether you choose natural, mechanical, or hybrid systems, it’s important to understand their types, benefits, and maintenance needs to make an informed decision. By taking into account factors like building design and climate, you can select a system that effectively balances efficiency, sustainability, and air quality.
Frequently Asked Questions :
What is the purpose of a ventilation system?
A ventilation system ensures healthy indoor air quality by removing pollutants, controlling moisture, and maintaining comfortable airflow.
What are the main types of ventilation systems?
The main types include natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation (exhaust, supply, and balanced systems), and hybrid ventilation systems.
How do I choose the right ventilation system for my building?
Consider factors such as building design, climate, energy efficiency, air quality needs, and compliance with local codes.
What is the difference between natural and mechanical ventilation?
Natural ventilation relies on passive airflow through openings, while mechanical ventilation uses fans and ducts to control airflow.
How often should a ventilation system be maintained?
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning filters and inspecting ducts, should be done every 3–6 months to ensure optimal performance.



Leave a Comment