Radiant floor heating is an increasingly popular and efficient method for warming indoor spaces. Unlike traditional forced-air systems that blow warm air through vents, radiant heating directly transfers heat to the floor and surrounding objects. This approach results in more consistent and comfortable heat distribution, enhancing both energy efficiency and overall comfort. There are several types of radiant floor heating systems, each with unique advantages and considerations. In this blog, we’ll delve into the different types of radiant floor heating systems, how they work, their pros and cons, and what to consider when choosing the right system for your needs.
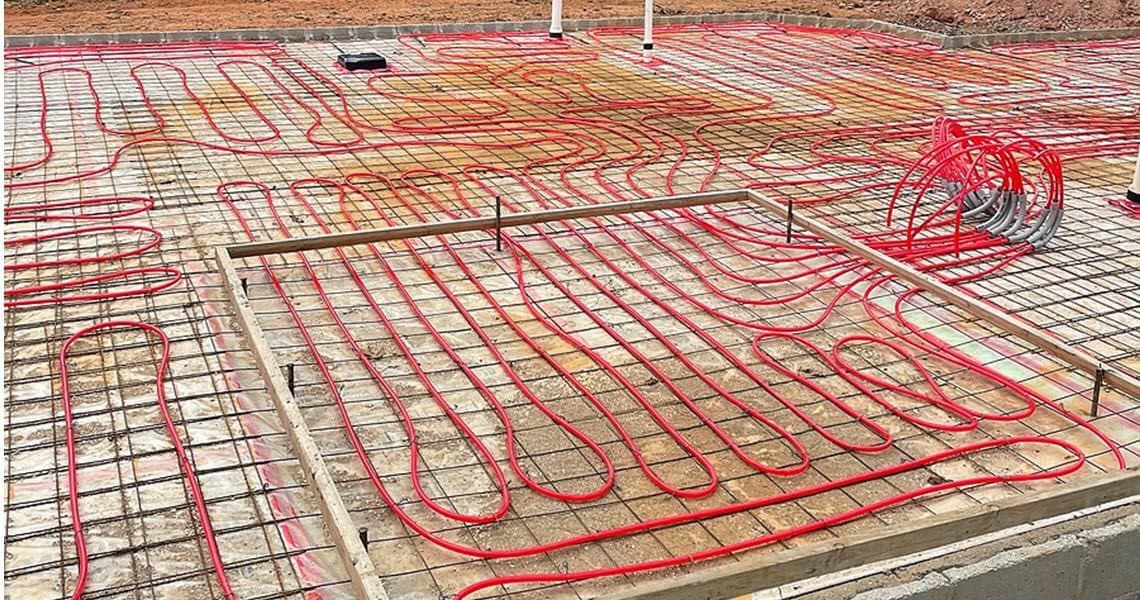
1. Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating
How It Works:
Hydronic radiant floor heating is the most prevalent type of radiant heating system. It operates by circulating warm water through a network of flexible pipes, usually made from PEX or other durable materials, that are installed in the floor. The water is heated by a boiler, water heater, or even solar energy, flowing through the pipes and releasing heat to the floor, which then radiates warmth into the room. This process creates a comfortable and evenly distributed heat throughout the space.
Advantages:
Energy Efficiency: Hydronic systems are known for their high energy efficiency, particularly when paired with modern, high-efficiency boilers or water heaters. Water’s excellent heat conductivity allows the system to warm large areas using less energy.
Long-Term Cost Savings: While the initial installation may be more expensive, hydronic radiant heating systems typically have lower operating costs compared to electric systems, especially in larger areas or entire homes.
Comfortable and Even Heat: The warmth generated by hydronic systems is more uniform, resulting in fewer cold spots compared to traditional heating methods.
Comfortable and Even Heat: Hydronic systems provide a more consistent heat distribution, minimizing cold spots compared to traditional heating methods.
Suitable for New Builds or Major Renovations: These systems are most effective when installed during the construction of a new home or during significant renovations that involve replacing or refinishing floors.
Considerations:
Complex Installation: Setting up a hydronic radiant floor heating system is more intricate and costly than other options, as it necessitates laying a network of pipes beneath the floor and requires a boiler or water heater as the heat source.
Maintenance: The boiler needs regular upkeep, and any problems with the piping can be challenging to fix, particularly if the pipes are embedded in the flooring.
Slower Response Time: Hydronic systems generally take longer to heat up and cool down than electric systems because they depend on heating water, which requires time.
2. Electric Radiant Floor Heating
How It Works:
Electric radiant floor heating systems utilize electrical cables or mats installed beneath the floor to generate heat. The system operates by allowing electricity to flow through the wires, which then warms the floor above. These systems are compatible with various flooring types, including tile, wood, and carpet.
Advantages:
Simple and Quick Installation: Electric radiant floor heating is relatively straightforward to install compared to hydronic systems. It’s particularly suitable for smaller areas, remodels, and retrofits, especially when you want to avoid disturbing the existing floor structure.
Lower Initial Cost: The initial expense for electric radiant floor heating is usually less than that of hydronic systems, making it a viable choice for those on a budget or with smaller spaces.
Faster Response Time: Electric systems heat up and cool down rapidly, offering more immediate warmth than hydronic systems.
Higher Operating Costs: Although electric radiant floor heating has a lower initial cost, it can become more expensive to run over time, especially in larger areas, since electricity typically costs more than gas or other energy sources used in hydronic systems.
Limited to Smaller Spaces: Because of the higher operating costs, electric radiant heating systems are typically more suitable for smaller rooms rather than for heating an entire home.
Energy Usage: Electric systems generally consume more energy than hydronic systems, which could lead to increased monthly utility bills, particularly in colder climates where heating is required for longer durations.
3. Air-Heated Radiant Floor Heating
How It Works:
Air-heated radiant floor heating systems are a less common and less efficient type of radiant heating. In this setup, warm air is circulated through ducts or channels beneath the floor. The air is usually heated by a furnace or air handler and then flows through the floor, warming the surface and heating the room.
Advantages:
Simpler Installation: Compared to hydronic and electric systems, air-heated radiant floor systems are relatively straightforward to install, especially in homes that already have ductwork.
No Water or Electrical Components: Unlike hydronic or electric systems, air-heated radiant systems don’t need complex plumbing or electrical setups, making them easier to maintain over time.
Considerations:
Less Efficient: Air-heated radiant floor systems are generally less efficient than other radiant heating options. Air is not as effective at transferring heat as water or electric cables, which can result in uneven heat distribution and higher energy use.
Space Heating: These systems are typically designed to heat the entire space rather than providing targeted heat to specific areas.
Poor Temperature Control: Since warm air rises, maintaining a consistent temperature with air-heated systems can be difficult. This can lead to problems with heat loss and uneven heating.
4. Solar Radiant Floor Heating
How It Works:
Solar radiant floor heating operates by utilizing solar panels to capture and convert sunlight into energy. This energy heats the water in a hydronic radiant heating system. The warm water then flows through pipes embedded in the floor, warming the space much like other hydronic systems, but with the added advantage of harnessing renewable energy.
Advantages:
Energy-Efficient and Environmentally Friendly: These systems are highly efficient, leveraging renewable solar energy to minimize dependence on fossil fuels or electricity. This makes them a great option for homeowners aiming to reduce their carbon footprint.
Lower Operating Costs: After installation, solar radiant heating systems incur very low operating costs since they depend on free solar energy.
Ideal for Sunny Climates: Solar radiant floor heating works best in areas that enjoy plenty of sunlight year-round.
Considerations:
High Upfront Costs: The initial investment for solar radiant floor heating systems can be substantial, covering the cost of solar panels, installation, and integration with a hydronic system. It may take several years to recover these costs through energy savings.
Weather Dependence: The effectiveness of solar energy can diminish in cloudy or cold climates, necessitating a backup heating system for days when sunlight is limited.
5. Electric Radiant Mats or Cables (Underfloor Heating)
How It Works:
Electric radiant mats or cables consist of thin sheets or coils of electric heating elements that are embedded in a flexible mat or mesh. These are installed beneath the floor surface, such as under tiles or hardwood flooring. When electricity flows through these elements, they produce heat, warming the floor.
Advantages:
Quick Installation and Convenience: Electric radiant mats or cables are straightforward to install, particularly during remodels or renovations when new flooring is being laid. They can be placed directly under the floor surface.
Even Heat Distribution: This system provides uniform heat distribution, making it especially effective in areas where precise heating is essential, like bathrooms or kitchens.
Great for Small Areas: These systems work well in compact spaces, such as entryways, bathrooms, or smaller rooms.
Considerations:
Higher Operating Costs: Similar to other electric radiant heating systems, the primary downside of mats and cables is their elevated operating cost. This system is more suitable for spot heating rather than heating an entire home.
Limited Use for Large Areas: Due to their energy consumption, electric radiant mats or cables are generally not recommended for larger spaces, as electricity costs can accumulate quickly.
Conclusion
Selecting the right radiant floor heating system involves several factors, including the size of the area to be heated, the climate, energy efficiency, and budget. Hydronic radiant heating is ideal for larger spaces and new constructions, offering long-term savings. Electric systems are more appropriate for smaller areas or retrofit installations, delivering quick heat at a lower initial cost. For environmentally conscious homeowners, solar radiant floor heating presents a green option, although it requires a higher upfront investment. Understanding the benefits, considerations, and optimal applications of each type of radiant heating system is essential for making the best choice.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of radiant floor heating systems?
The main types of radiant floor heating systems include hydronic (water-based), electric (cables or mats), air-heated, and solar radiant systems. Hydronic systems are usually preferred for larger areas, while electric systems work well in smaller spaces. Solar radiant systems harness solar energy, and air-heated systems distribute warm air through ducts located beneath the floor.
2. How does hydronic radiant floor heating work?
Hydronic radiant floor heating operates by circulating warm water through pipes that are installed under the floor. A boiler or water heater heats the water, and as it flows through the pipes, it releases heat into the floor, which then radiates upward, warming the entire room. This method is efficient and provides consistent heat across larger areas.
3. Is electric radiant floor heating more expensive to operate than hydronic systems?
yes, Electric radiant floor heating is typically more expensive to operate than hydronic systems, particularly in larger spaces. Although electric systems have lower installation costs, their operating costs tend to be higher because electricity is generally more expensive than gas or other fuels used in hydronic systems.
4. Can radiant floor heating be installed in existing homes?
Yes, radiant floor heating can be installed in existing homes, but the ease of installation depends on the type of system. Electric radiant heating systems are easier to retrofit into existing floors, while hydronic systems require more extensive work, including installing pipes and a boiler or water heater.
5. What are the benefits of solar radiant floor heating?
Solar radiant floor heating is both energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, as it utilizes renewable solar energy to warm the floor. Although the initial installation cost is higher, the long-term energy savings and reduced environmental impact make it an excellent choice for homes located in sunny climates.



Leave a Comment