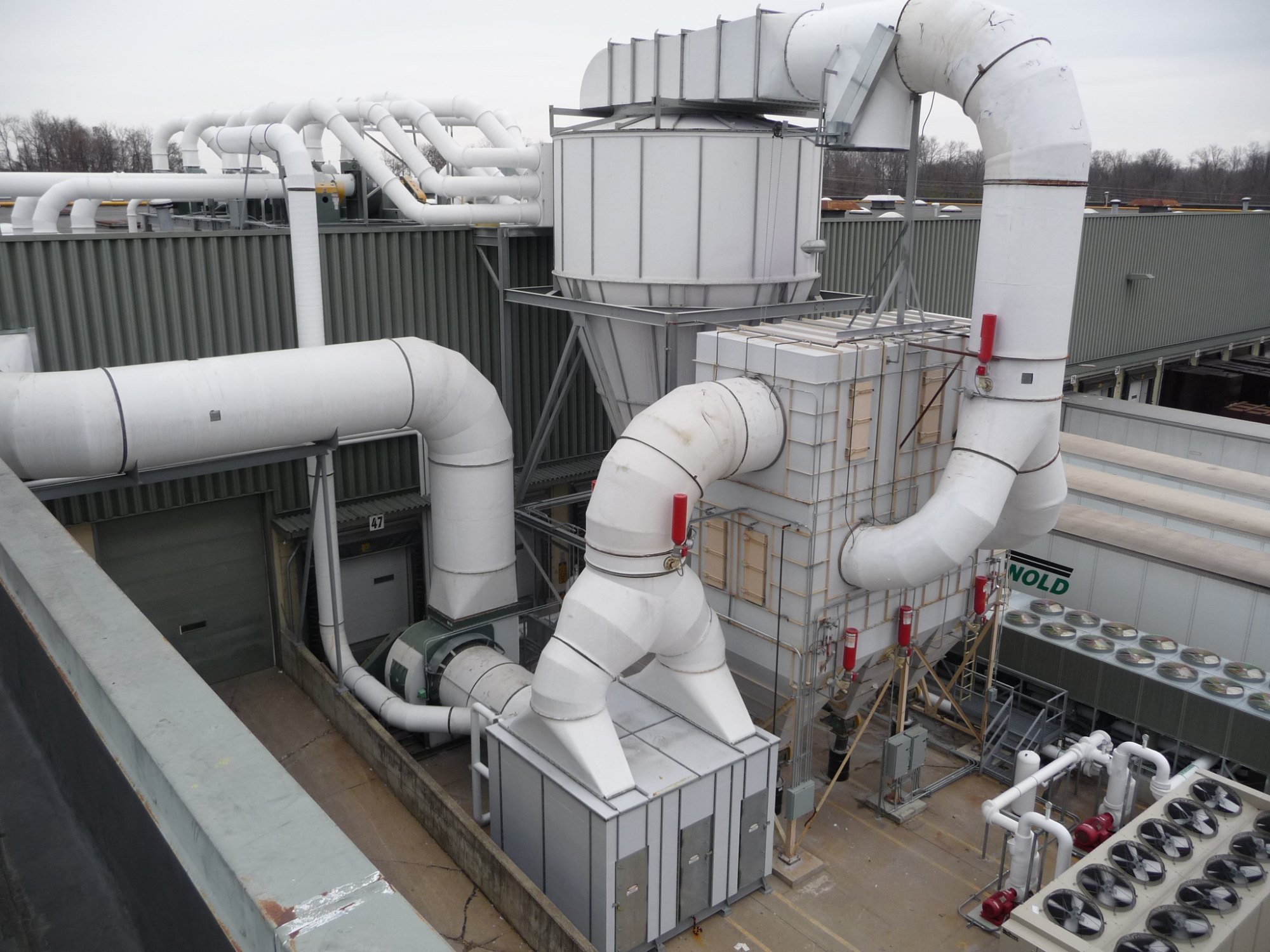
Industrial ventilation systems are used in various industrial settings to maintain the quality of air, ensure worker safety, and enhance productivity. These systems help control airborne contaminants, regulate temperature, and ensure a constant flow of fresh air. The following article looks into the various types of industrial ventilation systems, their functions, and their applications to guide industries on optimizing their workplace environment.
Importance of Selecting the Correct Ventilation System
The selection of an industrial ventilation system is based on the nature of the workplace, the types of contaminants present, and the specific requirements of the industry in the USA. A well-designed ventilation system not only ensures compliance with health and safety regulations but also improves overall operational efficiency.
Types of Industrial Ventilation Systems
1. Dilution Ventilation Systems
Overview:
Dilution ventilation is the introduction of fresh air into the workplace to dilute and reduce the concentration of airborne contaminants. This system is effective for controlling low-to-moderate levels of non-toxic pollutants.
Key Features:
- Suitable for large spaces with uniform contaminant distribution.
- It reduces the concentration of odors, fumes, and heat.
- Relatively simple to install and maintain.
Applications:
- Warehouses
- Assembly plants
- Storage facilities
2. Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV) Systems
Overview:
LEV systems capture contaminants at source, thereby preventing them from spreading into the place of work. These systems have hoods, ductwork, and fans that are used for direct extraction of harmful substances from the point of emission.
Key Features:
- Powerful in controlling hazardous substance.
- Does not allow the spread of contamination across the working area.
- Need for accurate design and position.
Applications:
- Welding operations
- Chemical processing units
- Spray painting booths
3. Natural Ventilation Systems
Overview:
Natural ventilation is the process, where air is circulated with the help of wind and thermal buoyancy through any open window, vent, or other opening. Although it is a cheaper affair, its performance is also highly dependent on the external weather.
Key Features:
Low operational costs
- Environment-friendly
- Less control over airflow.
Applications:
- Agricultural buildings
- Green houses
- Low-risk industries
4. Mechanical Ventilation Systems
Introduction
Mechanical ventilation uses fans and blowers to control airflow within a facility. Such systems are versatile and offer consistent ventilation without concerning oneself with external weather conditions.
- Highly adaptable to particular requirements
- Functions well in enclosed spaces.
- Can be combined with air filtration systems.
Applications:
- Manufacturing plants
- Pharmaceutical facilities
- Data centers
5. Hybrid Ventilation Systems
Overview:
Hybrid systems integrate natural and mechanical ventilation to maximize energy efficiency and performance. Hybrid systems switch between modes depending on environmental conditions and operational requirements.
Key Features:
- Energy-efficient solution
- Flexible and adaptive to changing needs.
- Initial setup can be complex.
Applications:
- Office buildings
- Industrial facilities with seasonal airflow needs
6. Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) Systems
Overview:
ERV systems recover energy from exhausted air and use it to condition incoming fresh air. This not only improves air quality but also reduces energy consumption.
Key Features:
- Improves energy efficiency.
- Reduces heating and cooling costs.
- Ensures a constant supply of fresh air
Applications:
- Food processing units
- Hospitals
- Laboratories
7. Fume Extraction Systems
Overview:
These systems are specifically designed to capture and remove harmful fumes. They are essential in industries where workers are exposed to toxic or corrosive gases.
Key Features:
- Specifically designed for gas and fume removal.
- Comprises high-end filter systems.
- Safety of workers working in dangerous atmospheres.
Uses:
- Chemical manufacturing
- Fabrication of metals
- Electronics
8. Ventilation Industrial Air Purifiers
Overview
This is a combination of air purifier and ventilation to ensure contamination-free and pure air. Such systems are needed for places requiring strict air purity.
Key features
- Dust, allergen, and pollutants removal
- May contain HEPA or activated carbon filters
- Very suitable for delicate operations
Applications
- Clean room
- Medical and healthcare facilities
- Food packaging establishments
Consideration for Selecting a Ventilation System
Nature of Contaminants:
Determine the nature and concentration of pollutants to decide on the system.
Airflow Requirements:
Determine the amount of airflow required based on the space and number of workers.
Energy Efficiency:
Select systems with energy-saving features to minimize operational costs.
Compliance:
Ensure that the system is compliant with OSHA and other regulatory requirements on air quality.
Maintenance Needs:
Select a system that is easy to maintain and has spare parts readily available.
Conclusion
Industrial ventilation systems are highly varied and designed for specific uses and issues. Familiarity with the different types of systems and applications will help a manufacturing industry design a safer, healthier, and more efficient workplace. Whether it is controlling hazardous fumes, improving air quality, or enhancing energy efficiency, choosing the proper ventilation system is an essential choice in any industrial facility.
Frequently Asked Questions about Industrial Ventilation Systems
What are industrial ventilation systems used for?
Industrial ventilation systems control airborne contaminants, temperature, and quality of air within an industrial working environment for safe working and meeting health standards.
How does a local exhaust ventilation system work?
The local exhaust ventilation system collects airborne contaminants from the source by the use of hoods, ductwork, and fans so that they cannot travel into the work environment.
What is the difference between natural and mechanical ventilation?
Natural ventilation relies on wind and thermal buoyancy. Mechanical ventilation makes use of fans and blowers that ensure constant flow regardless of weather conditions.
What industries would require energy recovery ventilation systems the most?
Food processing, healthcare (hospitals), laboratories, etc. require energy recovery ventilation systems to maintain high quality air and minimize energy consumption.
What should I consider when I choose an industrial ventilation system?
Consider factors such as the type of contaminants, required airflow, energy efficiency, compliance with regulations, and maintenance needs when selecting a ventilation system.



Leave a Comment