n recent years, geothermal heating has become a sustainable and cost-effective option for homeowners and businesses aiming to lower their energy usage while reducing their environmental footprint. As the world increasingly embraces eco-friendly energy solutions, geothermal heating systems are recognized for their capacity to deliver efficient, reliable, and renewable heat sourced from the earth’s natural resources. This article will delve into the basics of geothermal heating, its advantages, how it operates, and why it’s gaining traction as a green alternative to conventional heating systems.
What is Geothermal Heating?
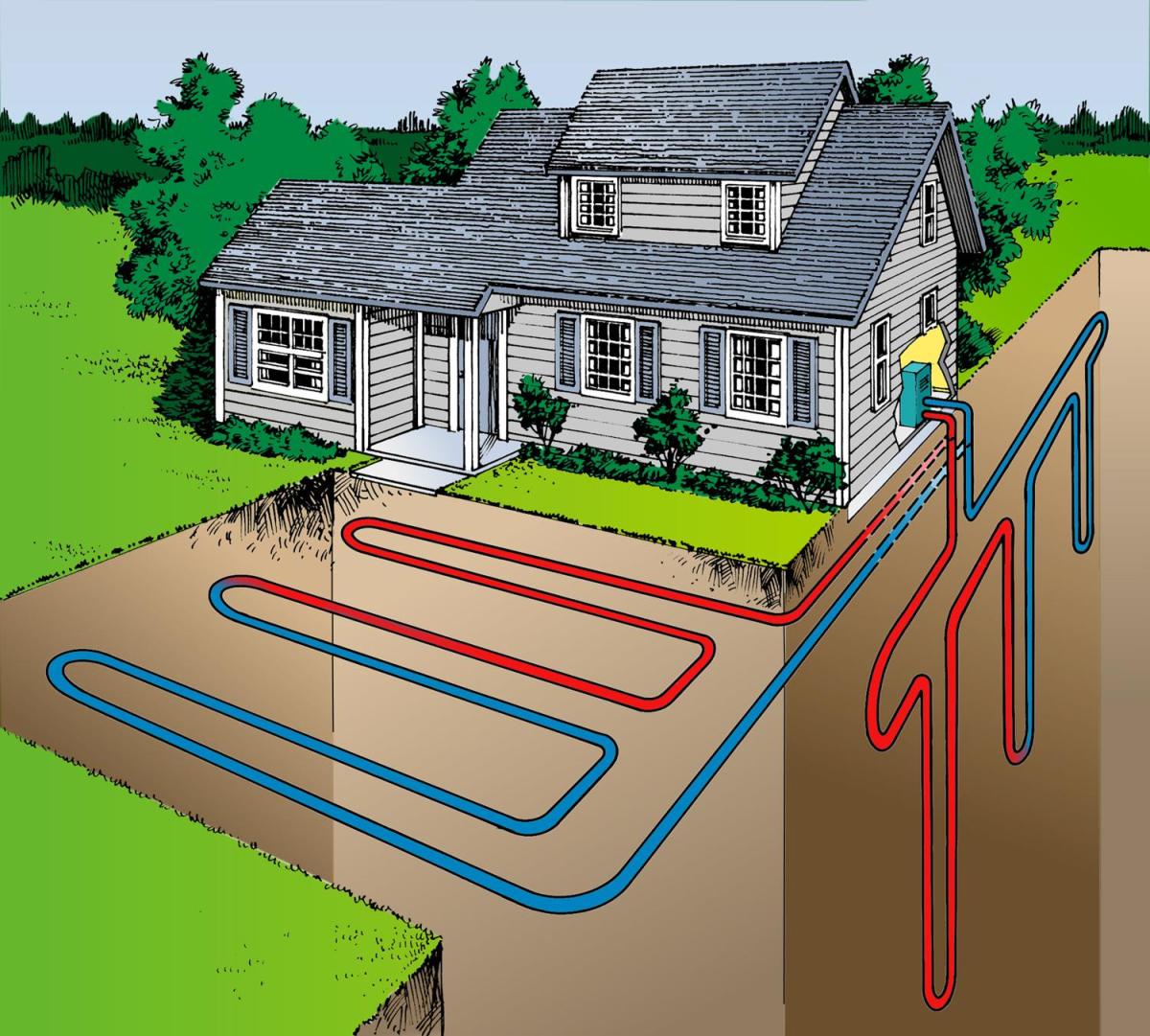
Geothermal heating utilizes the Earth’s consistent underground temperature to provide heating and cooling for buildings. Unlike traditional heating systems that depend on fossil fuels like oil, gas, or electricity, geothermal systems leverage the stable temperature found just below the surface of the Earth. Typically, the Earth maintains a temperature of around 50 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit (10 to 15 degrees Celsius) just a few feet underground, making it an ideal resource for both heating and cooling.
How Does Geothermal Heating Work?
Geothermal heating systems are made up of a heat pump, an underground network of pipes, and a heat exchanger. The process can be divided into three main stages:
Heat Absorption: Geothermal systems utilize pipes, commonly known as “ground loops,” that are buried underground. These pipes contain a heat transfer fluid (usually a mix of water and antifreeze) that circulates through the system. As the fluid moves through the loops, it absorbs heat from the Earth’s naturally stable temperature.
Heat Transfer: The heated fluid then returns to the heat pump located inside the building. The heat pump operates similarly to a refrigerator but in reverse. It employs a compressor to elevate the temperature of the heat from the fluid and transfers it into the building’s air.
Once the heat is transferred into a home or business, it is distributed through either a forced-air system or a radiant heating system, like underfloor heating. This method ensures consistent warmth during the colder months. In the summer, the system can be reversed to cool the building by pulling heat from the indoor air and sending it back into the ground.
Types of Geothermal Systems
There are various types of geothermal heating systems, each offering unique benefits based on the environment and building design. The primary types include:
1. Closed-Loop Systems: The most prevalent geothermal system, closed-loop systems consist of a network of pipes arranged either horizontally or vertically underground. These pipes are sealed, allowing the heat transfer fluid to circulate continuously.
- Horizontal Loops: Installed in trenches or shallow horizontal wells, these loops are best suited for properties with enough space for excavation. While horizontal loops are cost-effective, they do require a larger area for installation.
- Vertical Loops: These loops are drilled deep into the ground, making them ideal for properties with limited space. Although vertical loop systems tend to be more expensive to install due to the deep drilling required, they can be more efficient in specific conditions.
2.Open-Loop Systems: Open-loop systems utilize groundwater from a well or another water source as the heat transfer fluid. The water flows through the heat pump and is then returned to the ground or water source. These systems are less common because they depend on clean and plentiful water sources, but they can be very efficient when such resources are available.
3.Hybrid Systems: Hybrid systems merge geothermal heating with a traditional heating source, like a furnace or boiler. These systems aim to maximize efficiency by using geothermal energy when it’s accessible and switching to the conventional system when needed.
Advantages of Geothermal Heating
- Energy Efficiency: Geothermal systems are known for their impressive energy efficiency, often delivering three to four units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. This leads to lower utility bills and a decrease in energy usage compared to conventional heating methods.
- Environmentally Friendly: Since geothermal heating harnesses renewable energy from the Earth, it generates far fewer greenhouse gas emissions than heating systems that rely on fossil fuels. This makes it a sustainable option that can help lower your carbon footprint.
- Long-Term Savings: Although the initial investment for a geothermal system may be higher than that of traditional heating systems, the long-term savings can be significant. Geothermal systems typically have a long lifespan, often lasting 20-25 years for the heat pump and over 50 years for the ground loops, with minimal maintenance needed.
- Reliable and Consistent: Geothermal systems are exceptionally reliable, providing steady heating and cooling regardless of external weather conditions. Unlike air-source heat pumps that may struggle in extreme temperatures, geothermal systems can effectively maintain a comfortable indoor climate throughout the year.
- Reduced Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and a longer lifespan compared to traditional heating systems, geothermal systems require less upkeep. The underground loops are shielded from the elements, which minimizes wear and tear. Additionally, the heat pump, located indoors, is less vulnerable to harsh conditions.
- Government Incentives and Tax Credits: Numerous governments provide tax incentives, rebates, or grants to promote the installation of geothermal heating systems. These financial incentives can significantly reduce the initial costs and make geothermal technology more attainable for homeowners.
Is Geothermal Heating Right for You?
Geothermal heating is an excellent option for homeowners seeking an energy-efficient and eco-friendly heating solution. However, it might not be suitable for everyone. The upfront installation costs can be significant, ranging from $10,000 to $30,000 based on the system size and property, which can deter some homeowners. Nevertheless, these expenses are often balanced out by long-term energy savings.
If you reside in an area with a consistent underground temperature and have adequate space for installation (especially for horizontal systems), geothermal heating can be a fantastic choice. Well-insulated homes in regions with extreme weather conditions may also take advantage of the dependable and steady performance of geothermal heating.
Conclusion
As we strive for more sustainable energy options, geothermal heating emerges as a valuable solution for decreasing our dependence on fossil fuels while ensuring reliable and cost-effective climate control. By tapping into the natural energy beneath our feet, geothermal heating provides a cleaner, greener, and more efficient method for maintaining comfort in homes and businesses throughout the year. Whether you’re constructing a new home or contemplating a system upgrade, geothermal heating is definitely worth considering for its long-term advantages for both the environment and your finances.
Leave a Comment