Smart ventilation systems are transforming the way we ensure interior environmental quality and economies of energy. These sophisticated systems maintain an indoor atmosphere for healthier living while contributing to sustainability and cost savings. In this blog post, we have outlined applications in various settings, implementation trends, market trends, impact on sustainability, and what’s in the future for smart ventilation systems in detail.
Applications in Various Settings
Residential Spaces
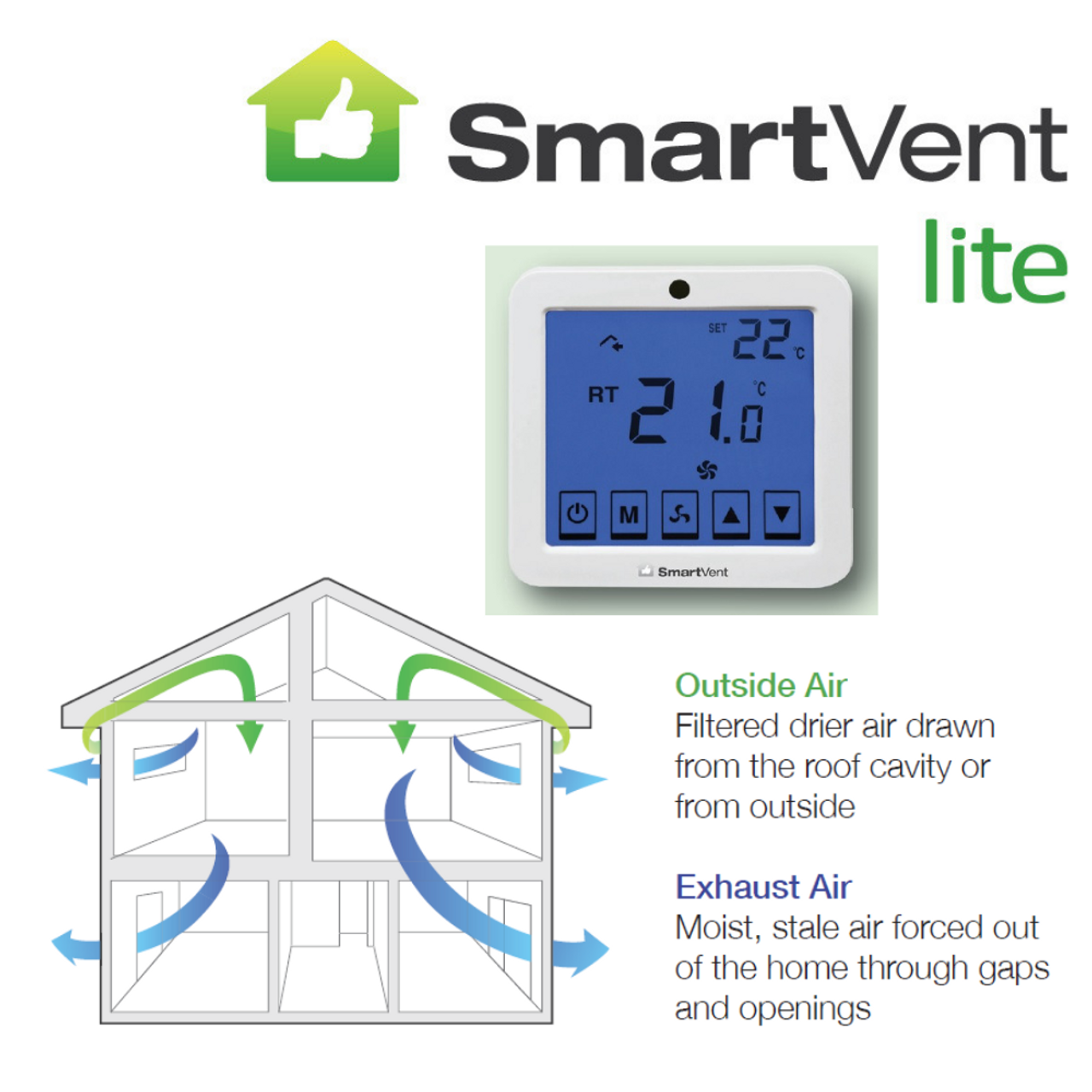
The most important role smart ventilation systems play in homes is to maintain the quality of air indoors. The systems monitor the level of pollutants in the air, humidity levels, and temperature and automatically regulate airflow to maintain a comfortable, healthy living space. For example, smart sensors can detect the carbon dioxide levels and increase ventilation when necessary to promote better respiratory health for its residents.
Commercial Buildings
In offices, malls, and other commercial locations, smart ventilation ensures optimized energy use with fresh air. Integration of the system with a building management system allows it to control airflow on the basis of occupancy and time of day for maximum efficiency in peak hours and saving energy at downtime.
Industrial Locations
Factories and warehouses are full of hazardous gases and dust. Smart ventilation systems are installed with advanced filtration technologies and real-time monitoring, ensuring the safety of workers. These systems detect harmful substances in real time and respond immediately to reduce risks and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals and clinics require precise air quality control to prevent the spread of airborne diseases. Smart ventilation systems in these settings ensure sterilized airflow, control humidity, and maintain optimal pressure levels to create a safe environment for patients and staff.
Implementation and Installation
Key Components of Smart Ventilation Systems
Sensors and Monitors: Detect air quality, temperature, and humidity.
Control Units: Centralized systems to regulate airflow.
Smart Filtration: The system is designed with advanced filters that remove allergens, dust, and harmful particles.
IoT Integration: The system allows remote access and automation through mobile applications.
Installation Process
Assessment: Assess the building’s ventilation needs, size, and existing systems.
System Design: Create a customized plan that integrates smart technology and adheres to energy efficiency standards.
Installation: Ducts, sensors, and control units will be installed with seamless integration into existing HVAC systems.
Testing and Calibration: The system will be rigorously tested for optimal performance.
Training and Upkeep: Instruct users in the use of the system, and maintain them regularly to enjoy long-term efficiency.
Common Problems
High installation cost: The initial installation of a smart ventilation system can be pricey.
Integration into old systems: Retrofitting is tricky and may cost more.
Upkeep: Keeping it efficient necessitates regular upkeep, which means operational costs could be higher.
Market Trends and Developments
Growing Demand for Smart Homes
The rise of smart homes has greatly increased the adoption of smart ventilation systems. Consumers are looking for convenience and energy savings, which makes these systems popular for modern households.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
Modern smart ventilation systems rely on AI and machine learning to predict airflow needs and optimize performance. For example, systems can learn usage patterns and adapt to seasonal changes automatically.
Integration with Renewable Energy
Most of these systems can integrate with solar panels and other forms of renewable energy sources to improve their sustainability levels. Smart ventilation systems running on renewable energy can significantly reduce their dependence on the grid while decreasing the costs associated with operation.
Compact and Modular Designs
The producers focus on compact and modular designs for easy installation and maintenance. They are suited to urban homes or small commercial places that do not have a considerable amount of installation space.
Smart Ventilation and Sustainability
Energy Efficiency
Smart ventilation systems are optimized to reduce energy wastage. They adjust ventilation rates according to occupancy, so that energy is not wasted in unoccupied spaces.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
By integrating with renewable energy sources and using energy-efficient components, these systems significantly reduce carbon emissions. This is especially important in commercial and industrial settings where energy usage is high.
Air Quality Improvement
These smart systems not only purify the air by removing pollutants and allergens but are beneficial for the health of humans and also ease out the environment in comparison to conventional methods of purification using much energy.
Harmonization with Green Building Certification Standards
Smart ventilation systems, being part of green building certification standards, such as LEED and BREEAM, are preferred options for a green conscious construction project.
Future of Smart Ventilation Systems
Increased Connectivity
The future of intelligent ventilation is robust connectivity with other smart devices. Systems will easily integrate to build a holistic, automated indoor environment from smart thermostats to lighting and security systems.
Self-Sustaining Development
Predictive maintenance innovations will enable systems to identify and solve issues before they occur. Self-cleaning filters and automated diagnostics will minimize the need for manual maintenance.
Affordability
The cost of smart ventilation systems is likely to reduce as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, and hence, reach a wider population.
Smart Cities
Smart ventilation systems will form a crucial component in the smart city. Through integration with urban infrastructure, such systems can help achieve city-wide energy efficiency and monitor air quality.
Personalized Ventilation
Future systems will offer personalized ventilation, adjusting airflow and temperature based on individual preferences. This could be particularly beneficial in shared spaces like offices and public buildings.
Conclusion
Smart ventilation systems are changing the face of indoor air quality and energy efficiency. They find applications in homes, offices, and industries to provide customized solutions for every type of requirement. With the ever-evolving technologies and increasing concerns for sustainability, these systems are likely to become an integral part of modern living. Investing in smart ventilation systems today will ensure a healthier and more sustainable future for the generations to come.
FAQs About Smart Ventilation Systems
1. What are smart ventilation systems?
Smart ventilation systems are advanced air quality management solutions that use sensors, IoT integration, and automation to optimize airflow, improve air quality, and reduce energy consumption.
2. How do smart ventilation systems save energy?
These systems monitor occupancy and air quality in real-time, adjusting ventilation rates only when needed, which significantly reduces energy wastage.
3. Can smart ventilation systems be integrated with existing HVAC systems?
Yes, most smart ventilation systems can be retrofitted to work with existing HVAC setups. However, the level of integration depends on the compatibility of the systems.
4. Are smart ventilation systems suitable for small homes?
Absolutely. Many compact and modular designs are specifically created for small residential spaces, offering both efficiency and ease of installation.
5. What maintenance is required for smart ventilation systems?
Regular cleaning or replacement of filters, software updates, and periodic system checks are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the system.


Leave a Comment