Radiant floor heating systems are often lauded for their energy efficiency, comfort, and ability to distribute heat evenly. However, like any home improvement project, these systems come with their own unique challenges and considerations. To make a well-informed decision, it’s crucial to evaluate the potential obstacles alongside the benefits. This article explores the challenges and considerations of radiant floor heating systems, focusing on installation, compatibility, costs, and long-term performance.
Understand Radiant Floor Heating Systems
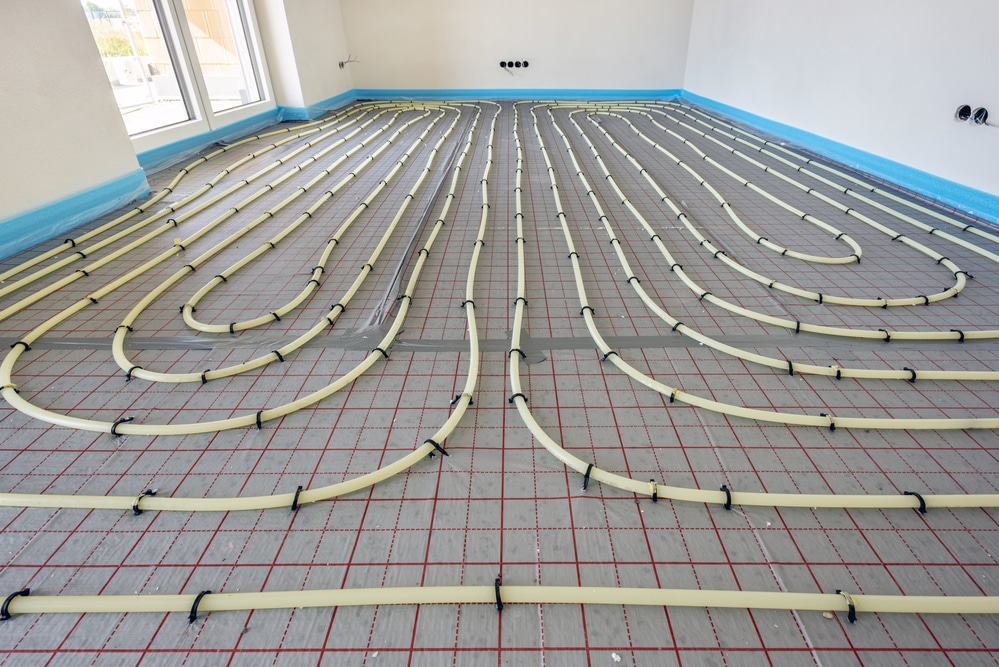
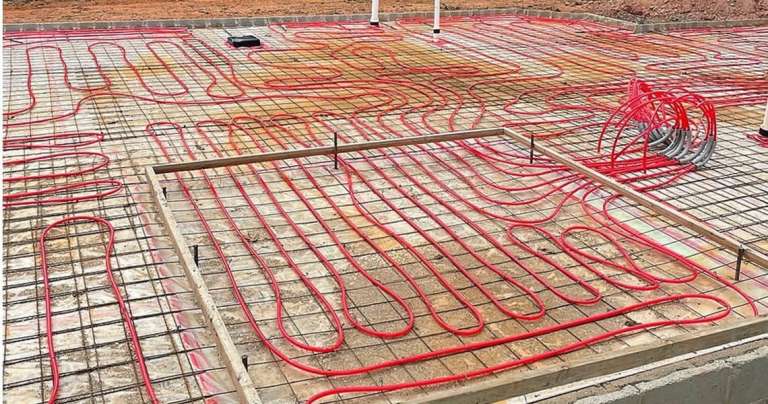
Radiant floor heating operates by utilizing electric coils or hydronic tubing placed beneath the flooring. These systems warm the floor, which then radiates heat upward, creating a consistently comfortable environment. While they are effective and innovative, the choice to install radiant heating involves several complexities.
Key Challenges of Radiant Floor Heating Systems
1. High Initial Installation Costs
One of the most significant hurdles to adopting radiant floor heating systems is their initial expense.
- Electric Systems: Generally more affordable for smaller spaces but can become expensive for larger areas. Installation costs typically range from $8 to $15 per square foot.
- Hydronic Systems: More cost-effective for heating an entire home but require a larger investment, with installation costs ranging from $10 to $20 per square foot, in addition to the cost of a boiler.
While these expenses may discourage some homeowners, they should be considered in light of potential long-term energy savings.
2. Flooring Compatibility Issues
Not all flooring materials work well with radiant heating systems.
- Optimal Materials: Tile, stone, and concrete are great conductors of heat, ensuring efficient transfer to the surface.
- Less Efficient Materials: Carpet and hardwood tend to insulate the floor, which can lower heating efficiency. To improve performance, special adjustments like thinner padding or specific wood types may be necessary, leading to increased costs. This limitation can restrict design options and result in higher expenses for appropriate flooring materials.
3. Retrofitting Challenges
Installing radiant floor heating in an existing home is more complex than adding it to new construction.
- Demolition Required: Retrofitting means removing the current flooring, which can be labor-intensive and costly.
- Floor Height Adjustment: Radiant systems raise the floor height, potentially requiring modifications to doorframes, baseboards, and thresholds. These challenges can make radiant heating a less feasible choice for many retrofit projects.
4. Energy Source and Efficiency Concerns
Although radiant heating is energy-efficient, its effectiveness relies on the energy source and system type.
- Electric Systems: These systems are generally less efficient for heating larger areas due to higher electricity costs.
- Hydronic Systems: Their efficiency depends on the boiler’s performance. Older boilers might offset the energy savings of the system. Homeowners need to ensure their energy source aligns with their sustainability goals and budget.
5. Slow Heating Response Time
- Radiant floor heating systems offer gradual warmth, which can be a drawback in situations where quick heating is needed.
- Forced-air systems deliver immediate heat, making them more suitable for areas with unpredictable weather changes. Radiant systems can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours to fully heat a room, particularly if insulation is lacking.
6. Complex Repairs
When a radiant floor heating system has issues, the repairs can be both invasive and expensive.
- Electric Systems: These are generally easier to diagnose, but you might need to lift sections of the floor to reach damaged cables.
- Hydronic Systems: Problems such as leaks or blockages can be tough to identify and resolve without disturbing the flooring.
It’s important to factor in these potential repair costs when planning your budget for the system.
7. Not Ideal for All Climates
Radiant floor heating systems work best in colder climates where heating is necessary for long periods.
- In warmer areas, the initial investment may not be worth it due to limited use.
- They are also less effective in large, open spaces with high ceilings, as heat tends to rise and escape more quickly.
Homeowners should evaluate their local climate and heating requirements before deciding on this system.
Key Considerations When Installing Radiant Floor Heating
Despite the challenges, radiant floor heating can be a valuable investment if you plan ahead.
1. Budget Planning
Think about not just the initial costs but also potential expenses for insulation, floor leveling, and system upkeep. Set aside an extra 10–15% of your estimated budget to handle any unexpected costs.
1. Professional Installation
Radiant floor heating systems need to be installed by skilled professionals. Hiring experienced installers ensures that the system is set up correctly and helps prevent future problems.
- Look for certified installers who specialize in electric or hydronic systems.
- Ask for detailed quotes that cover all related costs.
2. Insulation Is Key
- Good insulation is essential for maximizing efficiency and reducing energy loss.
- Place insulation beneath the radiant heating system to direct heat upward.
- Think about upgrading your home’s overall insulation for additional savings.
3. Smart Thermostat Integration
Investing in a smart thermostat can help you manage heating schedules and lower energy consumption. These devices let you program heating cycles according to your daily routine, optimizing energy use.
4. Evaluate Maintenance Needs
While radiant systems require less maintenance than traditional heating, they still need some care.
- Plan for annual inspections of hydronic systems to ensure the boiler, tubing, and pumps are working properly.
- Electric systems should be checked regularly for any wiring problems.
Benefits to Balance the Challenges
While radiant floor heating systems come with certain challenges, they also provide significant advantages:
- Comfort: Even heat distribution ensures there are no cold spots.
- Energy Efficiency: They offer considerable savings compared to traditional forced-air systems.
- Quiet Operation: There are no loud air ducts or fans to disrupt your peace.
- Improved Air Quality: They help minimize the circulation of dust and allergens.
These benefits make radiant floor heating an appealing choice for many homeowners who are ready to tackle the challenges.
Conclusion
Radiant floor heating systems represent a modern and energy-efficient heating option, but they do have their own set of challenges and considerations. Factors such as high installation costs, flooring compatibility, and repair complexities need to be thoroughly assessed before making a choice.
Nonetheless, with careful planning, professional installation, and a well-thought-out budget, radiant floor heating can deliver exceptional comfort and long-term value. By proactively addressing potential issues, homeowners can fully enjoy the numerous benefits of this innovative heating solution.
If you’re thinking about radiant floor heating, it’s wise to consult with experts to evaluate your home’s specific needs and create a tailored solution that effectively balances the challenges with the benefits.



Leave a Comment